Windows Scp Sync
Synchronizes content of a local directory with a remote one or vice versa or mutually.
The fastest way to transfer files and folders over SSH from Windows 10 to Linux is with the SCP tool. It works within the SSH protocol and allows users to quickly and easily transfer data right over the command-line from one computer to another! In this guide, we’ll show you how to use SCP on your Windows 10. We’ll cover two methods. WinSCP offers several ways to synchronize your remote and local directories. You can synchronize directories by manually uploading and downloading the changed files. For this you may find useful features like Synchronize browsing and Compare directories or transfer setting Newer and updated files only.
When the first parameter is local, changes from remote directory are applied to local directory. When the first parameter is remote, changes from the local directory are applied to the remote directory. When the first parameter is both, both local and remote directories can be modified.
When directories are not specified, current working directories are synchronized.
Unison is a file-synchronization tool for OSX, Unix, and Windows. It allows two replicas of a collection of files and directories to be stored on different hosts (or different disks on the same host), modified separately, and then brought up to date by propagating the changes in each replica to the other. Recently I upgraded my work laptop to Windows 7. At that time I didn't want to use the previous sync methods that I have blogged about. I wanted to use something simpler (read easier to install and maintain between different machines). After doing some research I settled on using winscp. Winscp supports folder sync operations.
Note: Overwrite confirmations are always off for the command.
Windows Scp Sync App
Switches:
| Switch | Description |
|---|---|
-preview | Preview changes only, do not synchronize. Transfer settings switches -permissions, -nopermissions, -speed, -transfer and -resumesupport have no effect. |
-delete | Delete obsolete files. Ignored for both mode. |
-mirror | Mirror mode (synchronize also older files). Ignored for both mode. |
-criteria=<criteria> | Comparison criteria. Possible values are time, size, either and none. Ignored for both mode. |
-preservetime | Preserve timestamp. Enforced by default unless -criteria is size or none. |
-nopreservetime | Do not preserve timestamp. Ignored unless -criteria is size or none. |
-permissions=<mode> | Set permissions (SFTP and SCP protocols only). |
-nopermissions | Keep default permissions. |
-speed=<kbps> | Limit transfer speed (in KB/s). |
-transfer=<mode> | binary ascii automaticTransfer mode: binary, ascii (text), automatic (by extension). |
-filemask=<mask> | <mask>[;<mask2>...]Sets file mask. |
-resumesupport= <state> | on off <threshold>Configures automatic resume/transfer to temporary filename. |
-rawtransfersettingssetting1=value1setting2=value2… | Allows configuring any transfer settings using raw format as in an INI file. E.g. to enable preserving of directory timestamps, use -rawtransfersettingsPreserveTimeDirs=1. The switch should come only after other parameters. |
Advertisement
Effective options: reconnecttime, failonnomatch
XML log elements: download (with local or both), upload (with remote or both), mkdir, touch (with remote or both), chmod (with remote or both and -permissions), rm (with remote and -delete)
When converting script to .NET Assembly, map synchronize command to Session.SynchronizeDirectories method.
Parameters mapping: Command parameter local remote both maps to method parameter mode, with values SynchronizationMode.Local, SynchronizationMode.Remote and SynchronizationMode.Both, respectively (Enumeration syntax in PowerShell is like [WinSCP.SynchronizationMode]::Local). Command parameter local directory maps to method parameter localPath. Command parameter remote directory maps to method parameter remotePath. You have to convert relative paths to absolute paths.
Switches mapping:
| Switch | Mapping |
|---|---|
-delete | Value true ($True in PowerShell) for method parameter removeFiles. |
-mirror | Value true ($True) for method parameter mirror. |
-criteria | Set method parameter criteria. Use SynchronizationCriteria.Time for time, SynchronizationCriteria.Size for size, SynchronizationCriteria.Either for either and SynchronizationCriteria.None for none. Enumeration syntax in PowerShell is like [WinSCP.SynchronizationCriteria]::Time. |
-permissions-nopermissions-transfer-filemask-resumesupport-speed=<kbps> | Converting transfer settings scripting switches to .NET assembly class TransferSettings. |
To emulate the (default) option batch abort mode, call TransferOperationResult.Check on method’s result. See also Capturing results of operations.
For example, following script snippet:
maps to following PowerShell code:

scp Linux command
Contents
Introduction
scp stands for secure cp (copy), which means you can copy files across ssh connection. That connection will be securely encrypted, it is a very secure way to copy files between computers.
scp uses by default the port 22, and connect via an encrypted connection or secure shell connection. (ssh for short)
You can use scp command in these scenarios:
- Securely copy files from remote computers to your computer
- Securely copy files from your computer to remote compueters
- Securely copy files from one remote computer to another remote computer
In the last case the traffic goes directly from one server to the other without passing through your system, that is a good thing if you have a slow Internet connection
You can use scp on Linux, Mac and Windows (using WinSCP). You may also want to check sftp
We will learn in this tutorial about the basic use of the command, and some useful examples and scenarios where you can use it.
Syntax
Explaining the complete syntax and every option of scp command is out of the scopy of this page, you can always enter a the command prompt
Or you can read it online here
We are going to explain the basic part of it:
- scp
- Is the command itself and tells the operating system to copy one or more files over a secure shell connection, better known as ssh connection.
- [[user@]host1:]file1
- The origin, where you specify the file or files to be copied, it can contain or not the information about a remote host, and it can also contain the information about the user owning the file or files in that remote host. If the user is not specified it will defaults to the current user in the machine where you are typing the command. If the host is not specified, it will look for the file locally using any given path.
- [[user@]host2:]file2
- The destination, where you specify the path where the files are going to be copied, once again, it can contain or not the information about the remote host and/or user in that host. Same as above if the user is not specified but a hostname is given it will defaults to the current username and will try to log in the remote server using that user. And in the same way as with origin, if the host is not specified, the files will be copied locally.
Just to clarify, you can avoid specifying both username and host in origin and destination, and the scp command will work just like the cp command, copying a local file to a local destination.
Examples
Copy one single local file to a remote destination
So, if you wan to copy the file /home/user/table.csv to a remote host named host.example.com and copy there to jane's home folder, use this command.
Copy one single file from a remote server to your current local server
Let's say now you want to copy the same file from jane's home folder in host.example.com to your local home folder.
Copy one single file from a remote server to another remote server
With scp you can copy files between remote servers from a third server without the need to ssh into any of them, all weight lifting will be done by scp itself.
Let's say now you want to copy the same table file from jane's home folder to pete's home folder in another remote machine.
Copy files between two remote server that are not in the same network
In the example above host and host2 can route traffic between them, either because they are on the same network or because there are routers in between that route the traffic. But in the case that they are in two different networks with no routers in between you will need to route traffic through the server issuing the command. This would be the scenario.
The command you will need is:
You need to issue the command in Host 0 and it has to have connection with the other two hosts
Copy one single file from a remote host to the same remote host in another location
This time, you will be copying from one host to the same host, but on different folders under the control of different users.
Copy multiple files with one command
You can copy multiple files at once without having to copy all the files in a folder, or copy multiple files from different folders putting them in a space separated list.
If the files are in different folders, just specify the complete path.
Copy all files of a specific type
This will copy all files of a given extension to the remote server. For instance, you want to copy all your text files (txt extension) to a new folder.
You can make use of wildcards in any way you want.
Copy all files in a folder to a remote server
This will copy all files inside local folder to the remote folder, let's see an example.
All files in local folder html, will be copied to backup folder in host.example.com
Copy all files in a folder recursively to a remote server
Same as the previous example, but this time it will copy all contentes recursively
Copy a folder and all its contents to a remote server
This time the folder itself is copied with all its contents and not only the contents. One more time we'll use an example.
This will result in having in the remote server this: /home/jane/backup/html/.... The whole html folder and its contentes recursively have been copied to the remote server.
Tips
We have seen the basic uses scp, now we will see some special uses and tricks of this great command
Increase Speed
scp uses AES-128 to encrypt data, this is very secure, but also a litle bit slow. If you need more speed and still have security, you can use Blowfish or RC4.
To increase scp speed change chipher from the default AES-128 to Blowfish
Or use RC4 which seems to be the fastest
This last one is not very secure, and it may not be used if security is really an issue for you.
Increase Security
If security is what you want, you can increase it, you will lose some speed though.
Limit Bandwidth
You may limit the bandwidth used by scp command
Where limit is specified in Kbit/s. So for example, if you want to limit speed at 50 Kbps
Save Bandwidth
Yoy can save bandwidth by enabling compression, let's see our example with compression.
Use IPv4 or IPv6
If you want to force the use of either IPv4 or IPv6 use any of these ones.
The above one is for IPv4, and below for IPv6.
Windows Scp Sync Software
Specify a port
If the remote server does not have ssh listening on default 22 port, you can make scp to use the port where the remote server is listening to:
Using the capital letter P you can make scp to use a port other than 22 which is the default for ssh. Let's say your remote server is listening on 2222.
Use verbose output
If you want to see what is happening under the hood, use the -v parameter for a verbose output
Move instead of copy files from one server to another
This is a question that was asked on server fault, and as it clarifies in that page, the best option is rsync, but if you can't use it here is a way to copy files with scp, and then if the copy was successful, you can delete the files from the origin.
This only works if you have configured your Linux ssh server to work with ssh-key instead of password
Copy files recursively preserving file attributes
If you want to copy a complete directory recursively and preserving file attibutes use this command:
-r copy directories recursively-p preserve file attributes
Windows
If you are working on a Windows powered computer, you can still enjoy scp in various ways, of course if you are a '*nix guy' you will prefer the command line, and you also have GUI tools available.
pscp
pscp is a shell command that works almost on Windows Shell almost the same way that scp works on Linux or Mac OS X, you first need to download it from this page, here is the direct link.
Once downloaded you can invoque it from the Windows command line, go to the start menu and click on run then write
And press ENTER, if you are on Windows 8.x hit the Windows/Super key and click on the magnifier lens, type cmd and hit ENTER.
Once in the command line, be sure to be in the directory where the pscp file was downloaded, or add that folder to your PATH, let's suppose the folder is your Downloads folder, run this command:
You will have to set that command every time you open a new command shell, or you can add the path permanently, how to do that is out of the scope of this article.
Below are the options of the command, you will see that the options available let you do almost everything.
Copy files from Windows to Linux
You can use scp command to copy files from Linux to Windows
Copy files from Linux to Windows
You can also copy files from Windows to Linux, using pscp from the Windows computer you can 'push' the files to the Linux, Max OS X or *BSD server.
Specify protocol
You can specify the protocol that scp command for Windows will use at the time of connection.
- -scp
- This will force pscp to use scp protocol
- -sftp
- This will force pscp to use sftp protocol, which is a newer protocol than scp protocol
WinSCP
WinSCP is a GUI version of scp, mainly for Windows, its development was started on 2.000 by Martin Přikryl and it is licenced under GNU licence.
It is not only a SCP client, but also SFTP and FTP client too.
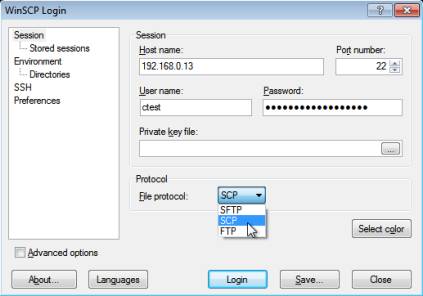
Screenshot
Below you can see a Screenshot of WinSCP
Main Features
Some of its main features are:
This feature will keep only the remote end in sync with the local, so any change made on the local side, will be updated in the remote side. But this will not work in other way. That is any change in remote will not be updated in local.
You can decide to delete remote files or not at the time of starting the syncronization. If you turn it on, any files deleted on local, will be deleted on remote, but if not, only new added files or changes to existing ones will be updated
You can also use the drag and drop feature to copy files from remote to local or viceversa
As you can see, you can optain the same basic functionality for Windows that Linux users already enjoy, and this is maybe the best and easieste way to transfer files from Windows and Linux and viceversa.
If you have suggestions or comments, write to contact at this domain.
Last edit on: April 4, 2020
By: Guillermo Garron